Front-end development is the process of creating the visual and interactive side of a website or application is the part that users see and directly engage with.
Every button clicked, menu opened, or page scrolled is powered by front end development.
At its core, what is front end development really about? It's about using HTML to structure content, CSS to style and format layouts, and JavaScript to add interactivity and dynamic behavior.
Modern frameworks and libraries such as React, Angular, and Vue.js further enhance development, allowing for faster, more scalable, and reusable code.
Beyond coding, front-end developers focus on user experience (UX), ensuring navigation is smooth, accessibility standards are met, and performance is optimized for speed and efficiency.
They act as a bridge between design teams and back-end developers, transforming static designs into interactive digital experiences.
This guide explores everything you need to know about front end development and engaging users with a seamless and intuitive experience.
What is Front End Development?
Front-end development focuses on the parts of a website or app that users see and interact with, such as text, buttons, links, animations, and layouts.

A front-end developer writes clean, efficient code, applies design principles, and ensures the product is accessible, user-friendly, and high-performing.
The Importance of Front End Development for Businesses
A well-crafted front end not only makes a strong first impression but also keeps visitors engaged, encouraging them to stay longer and interact more with the content. This directly impacts user retention and overall satisfaction.
Since a website or application often serves as the first point of contact between a business and its customers, the quality of its front end plays a vital role in shaping perception.
Many businesses invest in front end development with the same seriousness as they explore what are five marketing strategies that retailers spend half of their annual budget on?
An intuitive, user-friendly, and visually appealing interface communicates professionalism, builds trust, and reflects the brand’s identity.
Consistency in colors, typography, and design elements reinforces branding and strengthens recognition across digital platforms.
When aligned with strategies like corporate enterprise SEO service offers, front-end development ensures websites aren’t just visually appealing but also built to attract, engage, and convert visitors over time.
Front-End vs Back-End Development
To better understand the roles and responsibilities in web development, here’s a detailed comparison between front-end and back-end development, highlighting their distinct focuses, tools, and collaboration efforts.
| Aspect | Front-End Development | Back-End Development |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The part of web development that deals with everything users see and interact with. | The part of web development that focuses on the server-side, databases, and application logic. |
| Primary Focus | User experience (UX), design, and interactivity of the website or application. | Data management, server communication, and processing business logic for the application. |
| Languages/Technologies | HTML, CSS, JavaScript, frameworks like React, Angular, Vue.js, SASS, and front-end libraries. | PHP, Ruby, Python, Node.js, Java, databases like MySQL, MongoDB, PostgreSQL, Redis, APIs. |
| Core Responsibilities | Create the layout, structure, and interactive elements (buttons, forms, etc.).- Make websites responsive (work on mobile, tablet, desktop).- Ensure the website is visually appealing and user-friendly. | Develop server-side logic and databases.- Write APIs for data exchange.- Handle user authentication and session management.- Manage business logic for operations like transactions or processing requests. |
| User Interaction | Direct interaction with users.- Users interact with the UI elements such as buttons, forms, animations. | Indirect user interaction through server-side actions that provide data or services to the front-end. |
| Tools & Frameworks | Code Editors: VS Code, Sublime Text.- Design Tools: Figma, Adobe XD.- Frameworks/Libraries: React, Vue.js, Angular, Bootstrap. | Code Editors: VS Code, IntelliJ.- Server Tools: Apache, Nginx, Docker.- Databases: MySQL, MongoDB, PostgreSQL, Redis.- Frameworks: Django (Python), Express (Node.js), Spring (Java), Ruby on Rails. |
| Key Performance Factors | Page load speed.- Responsiveness on different devices.- Accessibility.- Aesthetics and design consistency.- User interaction (clicks, hover states, etc.). | Server uptime and reliability.- Fast data processing and retrieval.- Scalability to handle large amounts of traffic.- Data integrity and security. |
| Interaction with Front-End | Builds the visual and interactive elements that users see and use. | Provides the back-end infrastructure that supports and stores the data for the front-end. |
| Key Skillsets | HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.- Knowledge of frameworks (React, Angular, Vue.js).- Understanding of UX/UI principles. | Proficiency in server-side languages (Python, Java, PHP, etc.).- Database management and optimization.- Knowledge of APIs (REST, GraphQL). |
| Integration with External Services | Works with APIs provided by back-end developers to display dynamic data (e.g., weather updates, product lists). | Creates and manages APIs for front-end developers to consume (e.g., sending data to a database or performing actions). |
| Scalability & Maintenance | Focus on ensuring the website performs well on various screen sizes.- Ensures that visual elements are optimized for performance. | Ensures that the server infrastructure is scalable.- Focuses on handling high traffic loads and maintaining server uptime. |
| Collaboration with Other Roles | Works closely with UX/UI designers, back-end developers, and product managers to ensure a seamless user experience. | Collaborates with front-end developers to ensure that the back-end works effectively with the front-end interface. |
| Focus on Testing | Unit testing for individual components.- Integration testing for front-end flows (e.g., form submission).- Cross-browser testing. | Unit testing for API endpoints.- Load testing to handle server capacity.- Database testing for integrity and consistency. |
3 Core Technologies in Front-End Development
Front-end development is built upon three core technologies HTML, CSS, and JavaScript which together form the foundation of every modern website and web application.

1. HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
HTML is the structural backbone of the web. It provides the basic framework for a webpage by defining its content and organization.
Elements such as headings, paragraphs, images, links, tables, and forms are created using HTML. Without it, browsers would not know how to interpret and display text or multimedia content.
2. CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)
While HTML focuses on structure, CSS takes care of styling and design. It controls how elements look on the screen managing layouts, colors, typography, spacing, and even responsiveness across different devices.
With JavaScript, websites become dynamic and interactive, enabling complex features like real-time updates, animations, and interactive dashboards. Customized B2B eCommerce development services leverage JavaScript libraries and frameworks like React and Angular to enhance the interactivity of online stores.
CSS frameworks like Bootstrap or Tailwind CSS make it easier to design visually appealing and mobile-friendly websites quickly, much like how the best website builders for small business provide templated solutions for startups seeking quick deployment without advanced coding knowledge.
3. JavaScript
JavaScript is what makes websites dynamic and interactive. From simple tasks like form validation to complex features like real-time updates, animations, and interactive dashboards, JavaScript brings functionality to static pages.
With modern libraries and frameworks such as React, Angular, and Vue.js, developers can build highly scalable, user-friendly applications.
Together, these three technologies transform raw code into engaging, responsive, and interactive user experiences.
Explore Our Digital Transformation Services!
9 Key Frameworks in Front-End Development
Front-end frameworks provide developers with prewritten code, libraries, and components.
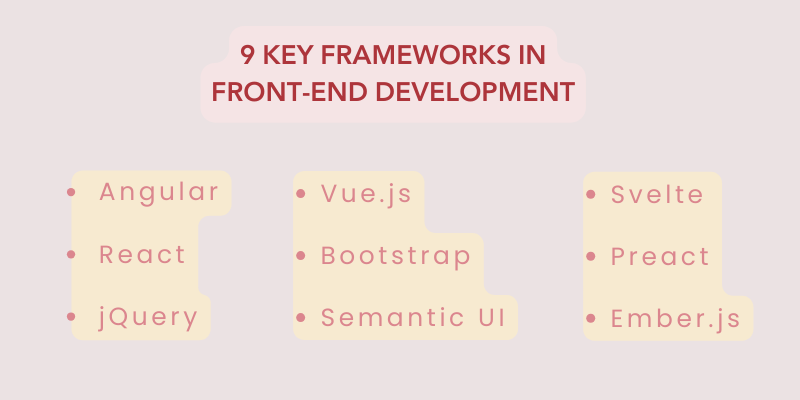
Instead of building everything from scratch, these tools speed up development with ready-made functions, UI elements, and drag-and-drop features for creating responsive, attractive applications.
1. Angular
Developed by Google, Angular is a powerful, open-source JavaScript framework that uses TypeScript for cleaner code. It follows the MVC (Model-View-Controller) architecture and supports modular development with dependency injection. Angular is ideal for building dynamic, large-scale applications.
2. React
Created by Meta in 2011, React is a widely used, component-based JavaScript library. It utilizes the Virtual DOM (VDOM) to efficiently update user interfaces, boosting performance. React is well-suited for developing single-page applications (SPAs) with reusable components.
3. jQuery
jQuery is a lightweight JavaScript library that simplifies DOM manipulation, event handling, and Ajax requests. It also enables applying effects like fade-in and fade-out. With its extensive plugin ecosystem, jQuery remains useful for quick, interactive solutions.
4. Vue.js
Vue.js is a progressive JavaScript framework focused on the view layer. It is easy to integrate with other tools, making it flexible for building modern interfaces and SPAs. Vue’s simplicity and adaptability make it popular among developers and particularly attractive to agencies like a tech marketing agency looking to deliver scalable front-end solutions without steep learning curves.
5. Bootstrap
Bootstrap is an open-source CSS and JavaScript framework for responsive, mobile-first design. It provides ready-to-use components like navigation bars, dropdowns, modals, and carousels. Its built-in responsive utilities simplify scaling layouts across devices.
6. Semantic UI
Semantic UI emphasizes human-friendly HTML for building responsive layouts. It comes with rich components and integrates easily with third-party tools, making front end development faster and more intuitive.
7. Svelte
Svelte is a compiler that converts components into highly optimized vanilla JavaScript at build time, reducing runtime overhead. Unlike React and Vue, which rely on the browser, Svelte shifts work to the build phase, delivering faster apps.
8. Preact
Preact is a lightweight alternative to React with a small footprint. It uses a thin Virtual DOM, real event handlers, and native browser features. Its minimal size means less code to download, parse, and execute, improving app speed.
9. Ember.js
Ember.js is an open-source JavaScript framework for large-scale, client-side applications. It follows the MVC pattern, using routes as models, Handlebars templates for views, and controllers to manage data flow. Ember is best for structured, complex apps.
User Interface (UI) & User Experience (UX) in Front-End Development
In front-end development, User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) work hand in hand to define how people perceive and interact with a digital product.
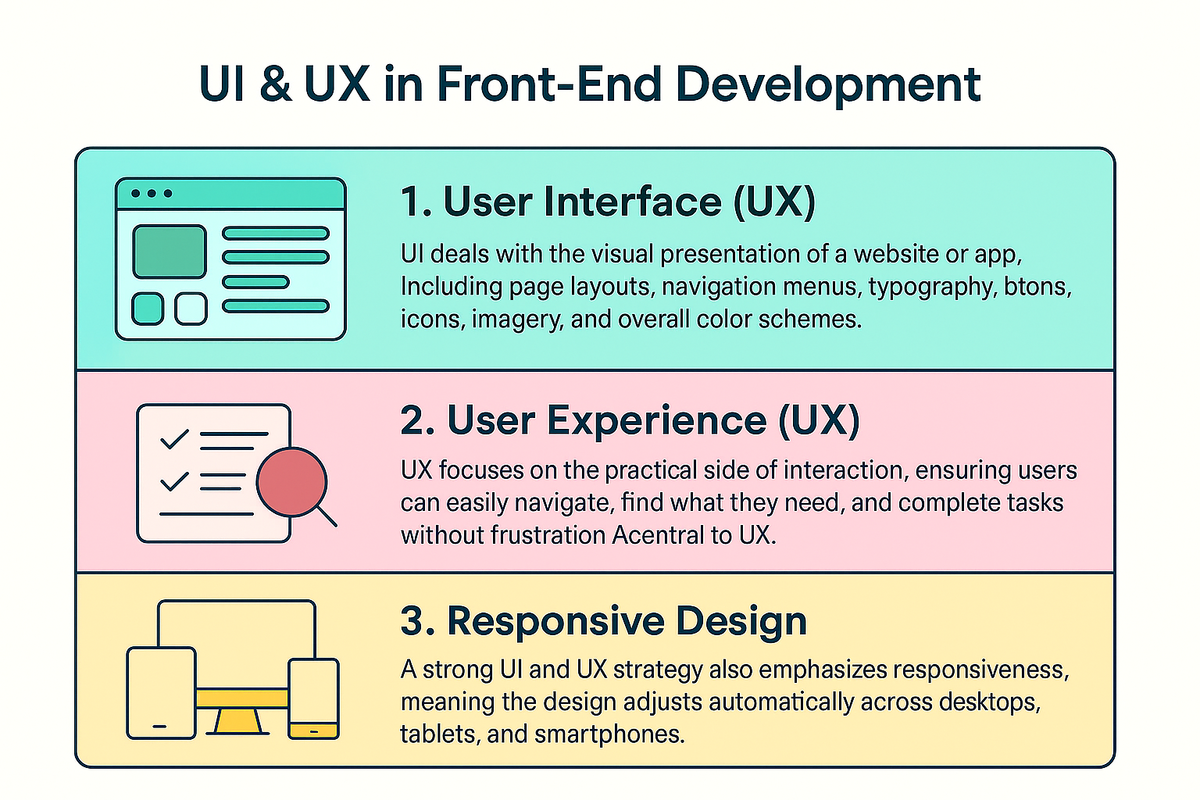
A well-designed website isn’t just about looking attractive, it must also feel smooth, intuitive, and functional for the end user.
1. User Interface (UI)
UI deals with the visual presentation of a website or app. This includes page layouts, navigation menus, typography, buttons, icons, imagery, and overall color schemes.
Developers also incorporate design elements like what are illustrations, infographics, and interactive media to enhance user engagement and convey brand storytelling more effectively.
A polished UI ensures that the design is visually appealing, consistent, and aligned with the brand identity. Front-end developers translate these design elements into functional code, bringing static mockups to life.
2. User Experience (UX)
UX focuses on the practical side of interaction. It ensures that users can easily navigate, find what they need, and complete tasks without frustration.
Smooth navigation, clear calls-to-action, and logical content flow are central to UX. Accessibility is also a crucial aspectensuring people with different abilities (visual, auditory, or motor impairments) can use the site seamlessly.
For instance, something as simple as knowing how to search a word on a website can drastically improve usability and empower users to find information quickly and independently.
3. Responsive Design
A strong UI and UX strategy also emphasizes responsiveness, meaning the design adjusts automatically across desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
This not only improves user satisfaction but also enhances SEO rankings, as search engines prioritize mobile-friendly websites.
When UI/UX Design & Branding are balanced, the result is a visually engaging, accessible, and user-friendly experience that keeps visitors engaged and encourages them to return.
Tools & Build Systems in Front-End Development
Front-end development goes beyond writing code it also involves using a variety of tools and build systems to ensure efficiency, collaboration, and optimized performance.
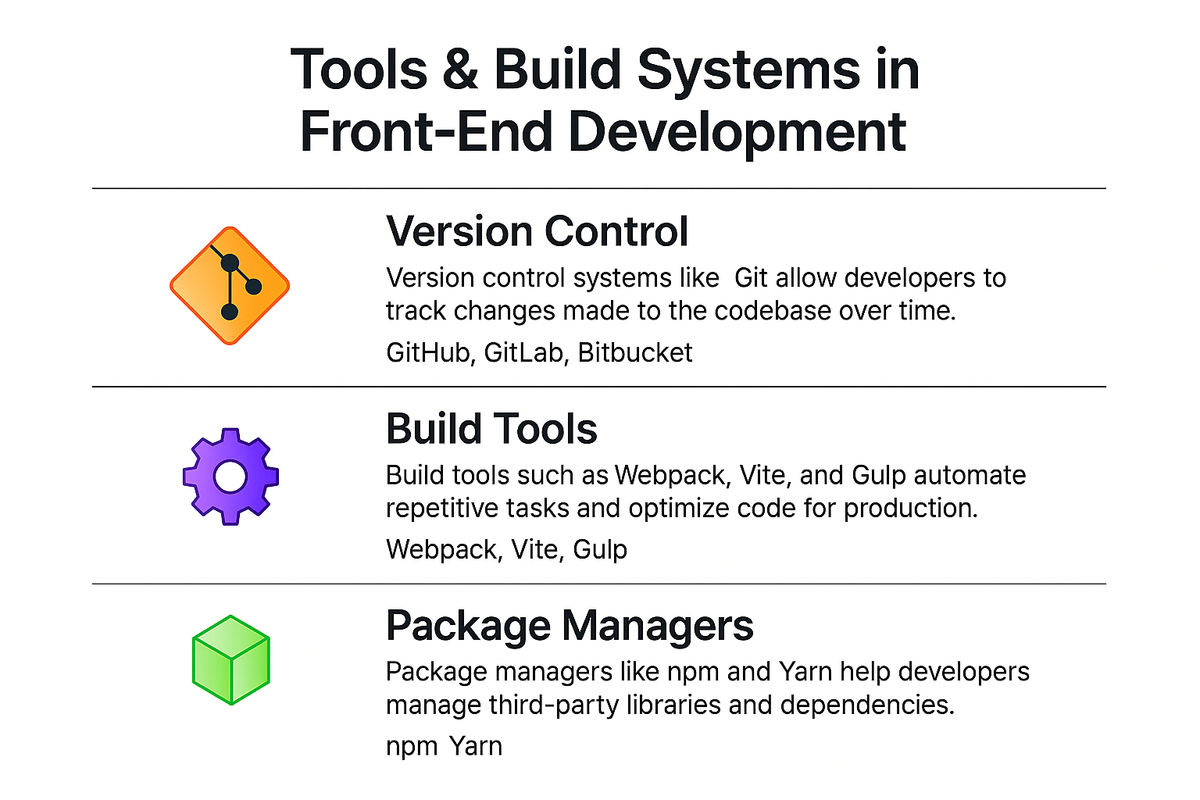
These tools help developers streamline workflows, maintain cleaner codebases, and deliver faster, more reliable applications.
Additionally, integration with SEO ranking report software helps front-end teams monitor the visibility and performance of websites in search engines, ensuring both code and content meet digital marketing goals.
1. Version Control
Version control systems like Git allow developers to track changes made to the codebase over time. Platforms such as GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket make collaboration seamless, enabling multiple developers to work on the same project without overwriting each other’s work.
Features like branching, merging, and pull requests improve teamwork and maintain code quality.
2. Build Tools
Build tools such as Webpack, Vite, and Gulp automate repetitive tasks and optimize code for production.
They handle processes like bundling JavaScript files, compiling SCSS/SASS into CSS, minifying code, and even live-reloading during development.
Front-end teams also use data such as Google keyword ranking insights to ensure content and design align with search visibility strategies.
This ensures that websites load faster and are more efficient when deployed.
3. Package Managers
Package managers like npm (Node Package Manager) and Yarn help developers manage third-party libraries and dependencies.
These tools, combined with systems like Product Information Management, streamline how teams manage both code and product content across eCommerce platforms.
Instead of manually downloading files, developers can install, update, or remove packages with simple commands, keeping projects consistent and easier to maintain.
Together, these tools form the backbone of modern front-end development, ensuring projects are scalable, collaborative, and performance-optimized.
Performance & Optimization in Front-End Development
Performance and optimization are crucial aspects of front-end development because even the most visually appealing website will fail if it loads slowly or is inaccessible to users.

A fast, efficient, and inclusive website not only improves the user experience but also boosts search engine rankings and overall engagement.
To achieve this, developers utilize tools like lazy loading, code splitting, and image optimization.
Techniques such as what is the digital marketing strategy that tracks users across the web? often complement front-end performance tools to analyze user behavior and enhance personalization, making websites not just fast but also smart in adapting to user needs.
1. Lazy Loading, Code Splitting, and Image Optimization
Lazy loading ensures that resources like images or videos are only loaded hen they are needed, reducing initial page load time.
Code splitting breaks large JavaScript bundles into smaller, manageable chunks that load on demand, improving responsiveness.
Additionally, image optimization using modern formats like WebP, compressing file sizes, or applying responsive image techniques significantly reduces bandwidth usage while maintaining visual quality.
2. Browser Caching and CDNs
Caching allows frequently accessed resources to be stored locally in a user’s browser, cutting down reload times.
Pairing this with a Content Delivery Network (CDN) ensures content is delivered from servers closest to the user’s location, minimizing latency and speeding up delivery worldwide.
Developers also use tools like the noindex tag when optimizing pages that should not be indexed by search engines, especially during development or for duplicate content.
3. Accessibility Standards (WCAG)
Performance isn’t only about speed it’s also about inclusivity. Following Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) ensures that websites are usable by people with disabilities, such as screen reader support, proper contrast ratios, and keyboard-friendly navigation.
By focusing on performance and optimization, developers create websites that are fast, reliable, and accessible to everyone.
Testing & Debugging in Front-End Development
Testing and debugging are essential parts of front-end development that ensure websites and applications run smoothly across different browsers, devices, and use cases.
Developers also consider how search engines interpret sites, often comparing DuckDuckGo vs Google to understand privacy-related search results and indexing behavior, which influences how debugging impacts SEO performance.
Without proper testing, even small bugs can lead to poor user experiences, broken functionality, or security vulnerabilities.
1. Debugging Tools
Front-end developers commonly use Chrome DevTools and similar browser-based tools to inspect code, monitor performance, and identify issues in real time.
These tools allow developers to analyze network requests, debug JavaScript errors, adjust CSS styling on the fly, and profile page performance all of which help in pinpointing and fixing problems quickly.
2. Testing Frameworks:
Automated testing frameworks like Jest, Mocha, and Cypress play a critical role in maintaining code quality. Jest is widely used for unit testing in JavaScript and React projects, Mocha provides flexibility for both unit and integration tests, while Cypress excels in end-to-end testing by simulating real user interactions.
Together, these tools help developers catch bugs early in the development cycle, reducing time and cost during production.
3. Cross-Browser Compatibility
Since users access websites from various browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge), ensuring cross-browser compatibility is vital.
Developers use testing tools and virtual environments to confirm that layouts, styles, and functionality remain consistent across platforms.
By integrating testing and debugging into their workflow, developers deliver reliable, user-friendly, and error-free applications.
Explore Our Web Design & Development Services!
Who Works in Front-End Development?
According to the 2024 Stack Overflow Developer Survey, 30.7 percent of developers consider themselves full-stack developers, working on both the front-end development and back-end development. Back-end developers represent 16.7 percent of the field, and 5.6 percent of developers reported their job duties as front-end developers. While both front-end and full-stack developers need to learn front-end skills, there are also other career paths within a front-end development team, such as a search engine optimization (SEO) strategist. Collaborating with an enterprise seo consultant can further optimize a website’s front-end by ensuring elements like site structure, metadata, and content hierarchy improve search engine rankings, driving more traffic to business platforms.
Explore these roles, their job outlook, and the average salary for each in the U.S. below.
Front-End Developers
- Average annual salary in the US (Glassdoor): $81,893
- Job outlook (projected growth from 2023 to 2033): 8%
What is front-end development? As a front-end developer, you will focus on the design side of web development, creating the visual aspects that users interact with directly. In this role, you’ll write code using technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to build layouts, navigation, and interactivity for websites and applications. You’ll collaborate with back-end developers and UX/UI designers to ensure a seamless and engaging user experience.
Full-Stack Developers
- Average annual salary in the US (Glassdoor): $96,070
- Job outlook (projected growth from 2023 to 2033): 8%
As a full-stack developer, you will have the ability to work on both the front-end development and back-end development of projects. Your responsibilities will vary depending on the size and scope of the project, but you may work on designing and coding the front-end of the site or application, or focus on back-end tasks like managing databases and programming server-side logic.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Strategists
- Average annual salary in the US (Glassdoor): $80,235
- Job outlook (projected growth from 2023 to 2033): 8%
In the role of an SEO strategist, your focus will be on helping your client’s website rank higher on search engines like Google. What is front-end development's connection to SEO? The front-end development of a website, such as the layout and content structure, plays a significant role in ensuring the site is optimized for search engines. As an SEO strategist, you will research keywords, implement link-building strategies, and optimize the website's technical aspects to improve its visibility and ranking in search engine results.
FAQs: What is Front End Development?
What is HTML? Is it front-end or back-end?
HTML is a markup language used to structure content on the web. It is a core technology for front-end development, meaning it's used for creating the structure of a website or web application that users interact with directly.
What is front-end development?
Front-end development refers to the part of web development that focuses on the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) of a website. It involves using technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create interactive and visually appealing websites that users can see and interact with directly.
What is an example of front-end development?
An example of front-end development would be building the layout of a website using HTML, styling it with CSS, and adding interactive elements such as buttons, forms, and animations using JavaScript. For instance, creating a responsive navigation bar that adapts to both desktop and mobile views.
What are the skills required for front-end development?
For front-end development, you need to learn HTML for structuring content, CSS for styling, and JavaScript for adding interactivity. Additionally, you should become familiar with version control (Git), browser developer tools, and responsive design practices. It’s also helpful to know about build tools, like npm scripts or Webpack, to streamline the development process.
What are the core technologies I should learn first for front-end development?
First, focus on front-end development fundamentals:
- HTML for the structure
- CSS for styling
- JavaScript for interactivity.
After that, learn version control (Git) and become comfortable with using browser developer tools for debugging and optimizing your code.
Do I need to learn a framework for front-end development?
While it's not absolutely necessary at first, learning a modern front-end framework like React, Vue, or Angular can accelerate development and help build scalable, maintainable projects. It’s recommended to start with the basics and then move on to frameworks as your projects grow in complexity.
What is responsive web design in front-end development?
Responsive web design is a front-end development technique used to ensure that web pages are adaptable to different screen sizes and devices. This is done through flexible layouts, fluid grids, and media queries, allowing websites to provide a good user experience across a wide variety of devices, from mobile phones to desktops.
What role do build tools play in front-end development?
Build tools in front-end development (like npm scripts, Webpack, or Vite) automate tasks such as bundling, minification, testing, and live-reloading. These tools help optimize workflows, making the development process more efficient and allowing for faster development cycles.
How do I optimize front-end performance?
To optimize front-end performance, focus on techniques like minimizing assets (e.g., images, JavaScript files), lazy-loading content, and using efficient rendering strategies. You should also optimize images, enable compression, and leverage caching and code-splitting to enhance load times and user experience.
How do I test front-end code?
Front-end development testing can be done using various tools to ensure quality and functionality. Unit tests focus on small pieces of logic, integration tests handle interactions between components, and end-to-end tests simulate user flows. Popular testing tools include Jest for unit tests, Cypress for integration tests, and Playwright for end-to-end testing.
Conclusion
What is front-end development? It is crucial for creating engaging, interactive, and user-friendly digital experiences. It blends technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript with modern frameworks to build responsive applications. Beyond coding, it focuses on UI and UX, ensuring websites are visually appealing, accessible, and intuitive across all devices. Performance optimization techniques like lazy loading, code splitting, and caching, along with rigorous testing, ensure efficiency and reliability. Front-end developers transform creative ideas into functional, high-performing web experiences, optimizing for performance, scalability, and accessibility. At Centric, front-end development goes beyond just visuals, it's about delivering seamless, user-centric web experiences that drive business success.