Software development is the methodical process of transforming ideas into scalable systems that solve real-world problems. It covers a wide range of disciplines, from software application development and IT software development to bespoke solutions for business operations. In simple terms, software is a collection of programmed instructions that enable computers to perform specific tasks.
Understanding what is software development is key to realizing how intuitive user interfaces, robust enterprise platforms, and tailored digital tools are created. These tools power everything from customer apps and internal dashboards to automation workflows and artificial intelligence integrations.
From intuitive user interfaces to robust enterprise platforms, development is the force that turns abstract needs into tangible digital assets. These tools power everything from customer apps and internal dashboards to automation workflows and artificial intelligence integrations.
What Is Software Development?
Software development is the process of designing, creating, testing, and maintaining software applications. These bespoke custom application could be for various purposes: web apps, mobile apps, enterprise systems, or even embedded systems for IoT devices. The primary goal of software development is to create functional software that meets the needs and requirements of users.
Software development is a systematic approach, with distinct stages that include planning, coding, testing, and deployment. Over the years, it has evolved into a multi-faceted discipline, incorporating a range of methodologies, tools, and technologies to enhance speed, efficiency, and scalability.
Explore Our Mobile Applications Service
Why Software Development Is Crucial?
From backend utility to business catalyst? There was a time when software primarily served as a back-office tool, handling data entry, managing files, or supporting accounting functions. Fast forward to today, and its role has evolved into something far more strategic.
Software now underpins every aspect of modern business, from how companies connect with customers to how they deliver services and scale operations. This transformation has been fueled by exponential growth in software investment. In the 1980s, global software spend was measured in the low billions. By 2021, that figure had grown to approximately $517 billion, demonstrating the shift of software from operational support to a core driver of business value.
1. The Rise of SaaS and Cloud-Native Solutions
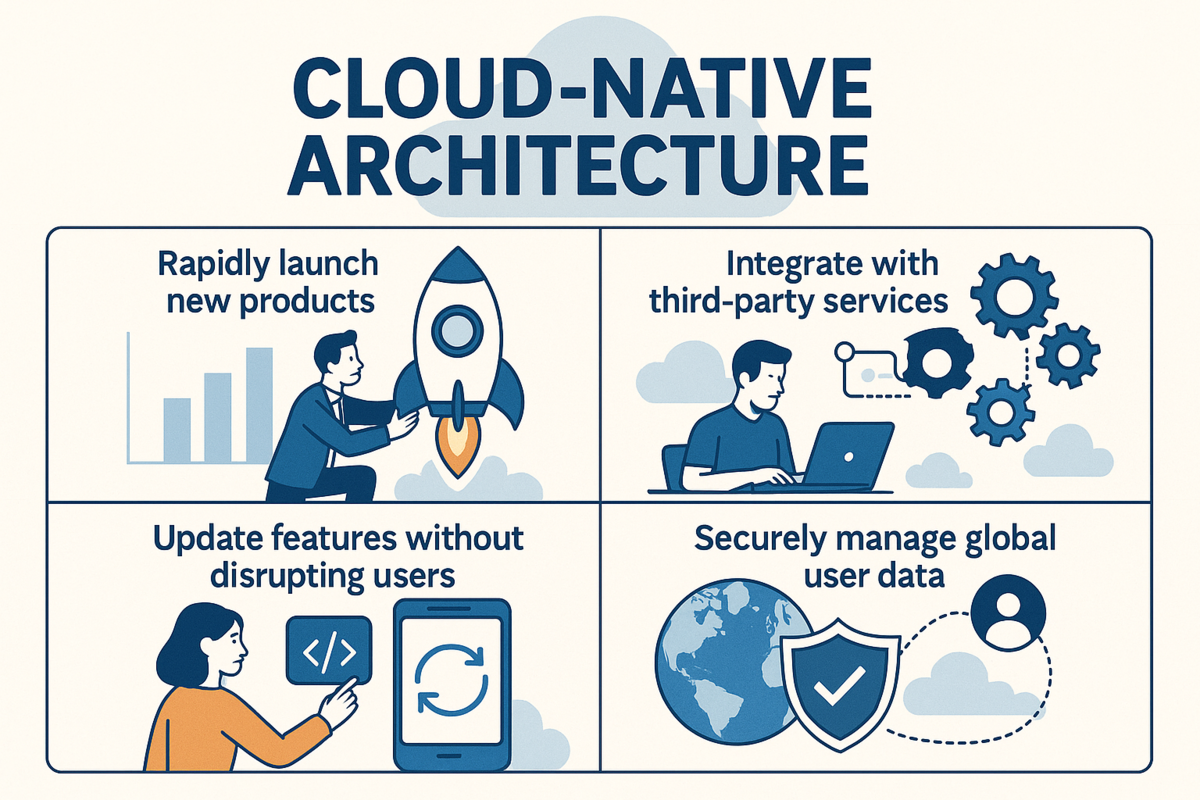
One of the most impactful evolutions in software development has been the emergence of Software as a Service (SaaS).
Instead of purchasing and manually installing software, companies now access cloud-based platforms that are constantly updated, easily scalable, and integrated across multiple devices and departments.
This shift isn’t just a trend, it’s an economic transformation. The SaaS market is forecasted to surpass $1.1 trillion by 2032, reflecting the global demand for agile, cloud-first solutions that reduce infrastructure costs and improve access.
Cloud-native architecture also enables companies to:
- Rapidly launch new products
- Integrate with third-party services
- Update features without disrupting users
- Securely manage global user data
2. Competitive Differentiation Through Proprietary Software
In an increasingly saturated digital market, off-the-shelf tools can only take you so far.
According to research by McKinsey & Company, businesses that outperform their competitors are 95% more likely to build proprietary software tailored to their specific needs.
Custom-built platforms empower companies to:
- Automate unique workflows
- Integrate deeply with internal systems
- Deliver exceptional user experiences
- Maintain complete control over their roadmap
This approach isn't just for tech companies. Even traditional industries like manufacturing and logistics are investing in proprietary systems to outperform rivals and accelerate innovation.
3. Industry Use Cases: Software at Work
Custom software development is transforming how industries operate, from real-time automation to personalized digital experiences.
1. Manufacturing: Manufacturers use custom-built software to automate production lines, manage real-time inventory, and forecast demand using machine learning.
2. Oil & Gas: In Oil & Gas operations, software development helps monitor equipment, manage field assets, and ensure environmental compliance.”
3. Healthcare: Healthcare providers leverage software for patient portals, appointment scheduling, electronic health records (EHR), and telemedicine integration.
4. Finance: Financial institutions rely on software for fraud detection, automated underwriting, mobile banking, and algorithmic trading.
5. Food & Beverage: Restaurants and packaged goods brands use custom software to streamline Food and beverage inventory, manage loyalty programs, and automate food safety tracking.
How Software Development Works?
The Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) refers to the stages involved in software development, from the initial idea to post-deployment maintenance. Understanding the SDLC helps in ensuring that the development process is systematic and effective. The Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) outlines the process of building software in structured stages:
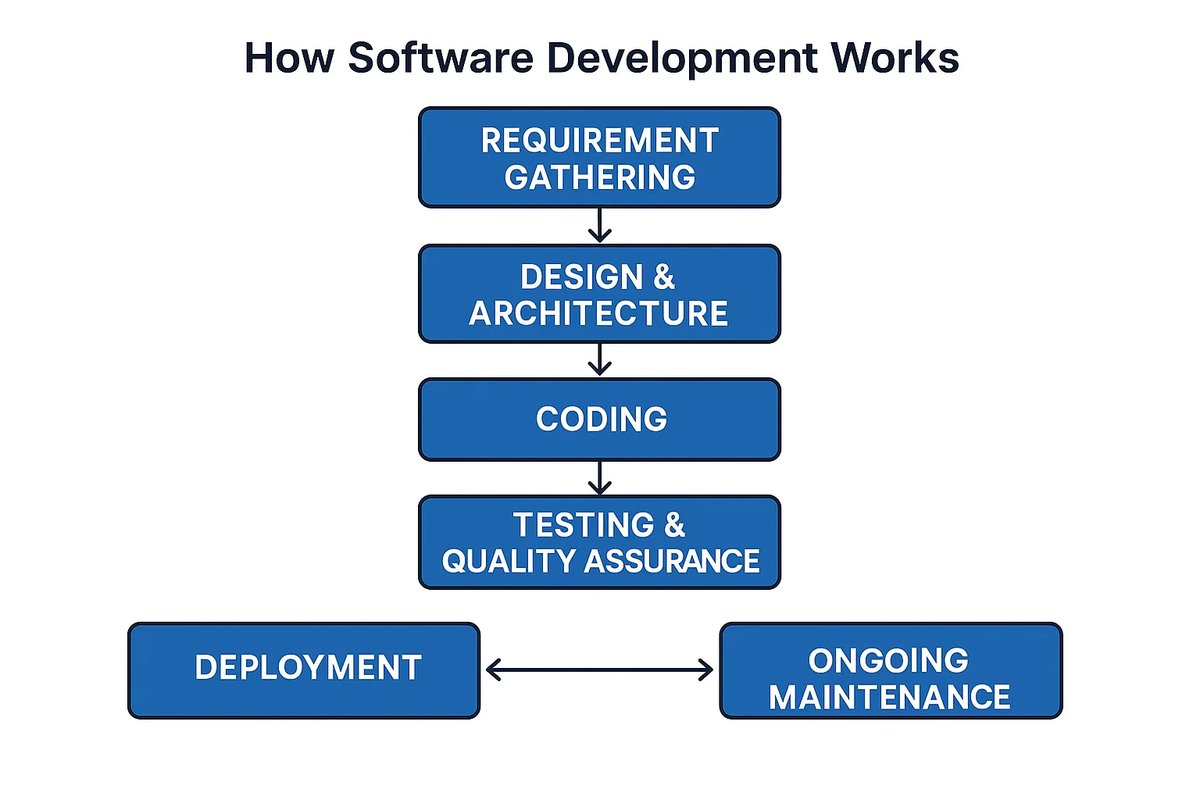
1. Planning and Requirement Gathering
The first phase of software development involves gathering requirements from stakeholders, including users, business leaders, and product managers. The goal is to understand what the software is expected to do and document these requirements in a clear and structured manner.
Key Activities:
-
Conducting stakeholder interviews
-
Analyzing business requirements
-
Defining the project scope
2. Design
Once the requirements are clear, the next phase is to design the system. This includes system architecture, database design, and user interface (UI) design. The design phase is critical because it lays the foundation for how the software will be structured.
Key Activities:
-
Creating system architecture diagrams
-
Designing wireframes and UI layouts
-
Choosing programming languages and frameworks
3. Development
The development phase is where the coding happens. Developers write the actual code based on the design and requirements. This is the longest phase in the SDLC, and it typically involves collaboration among various team members, including front-end developers, back-end developers, and database administrators.
Key Activities:
-
Writing the software code
-
Developing features and functionalities
-
Integrating APIs and third-party services
4. Testing
Testing is an essential part of the development process. It ensures that the software meets the specified requirements and works as intended. Bugs and issues identified during testing are reported and fixed before the software goes live.
Key Activities:
-
Unit testing: Testing individual components
-
Integration testing: Ensuring that different parts of the software work together
-
User acceptance testing (UAT): Verifying the software’s functionality against user requirements
5. Deployment
Deployment is the process of making the software available to users. Depending on the type of software, deployment could involve installing it on users’ devices, deploying it on a web server, or distributing it through app stores.
Key Activities:
-
Preparing the production environment
-
Deploying the software to the live environment
-
Training end-users on how to use the software
6. Maintenance
After deployment, the software enters the maintenance phase. This involves fixing bugs, updating the software, and improving its performance over time. Continuous feedback from users helps guide this phase.
Key Activities:
-
Providing software updates
-
Addressing user feedback
- Monitoring the software’s performance
6 Types of Software Development
Understanding different categories of software development helps businesses align technology with objectives. Key types include:
- Application Development – Builds user-facing software for web, mobile, or desktop.
- System Software Development – Develops operating systems and hardware-level programs.
- Embedded Development – Creates software within physical devices like appliances or cars. In the Automotive Industry, embedded development powers vehicle telematics, infotainment systems, and advanced driver-assistance features.
- Enterprise Software – Custom platforms such as CRMs or ERPs tailored to business workflows.
- SaaS & Cloud Development – Hosts applications in the cloud, improving flexibility, scalability, and enabling progressive web solutions for cross-device access.
- DevOps Engineering – Focuses on deployment automation and infrastructure resilience.
By tailoring these solutions, organizations can eliminate inefficiencies, scale effortlessly, and respond to market changes faster than ever.
6 Main Software Development Methodologies
This table outlines the different software development models, each with its unique approach and methodology. It provides an overview of when to use each model and the key benefits they offer for various types of projects.
| Development Model | Description | When to Use | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waterfall | Linear, sequential approach where each phase must be completed before moving on to the next. | Best for small projects with well-defined requirements. | Simple to understand, clear milestones. |
| Agile | An iterative process where work is done in small, incremental cycles or sprints. | Best for projects with changing requirements. | High flexibility, frequent feedback. |
| Scrum | A subset of Agile, focused on delivering software in short sprints with daily stand-up meetings. | Suitable for large teams working on complex projects. | Enhanced collaboration, quick deliverables. |
| DevOps | Focuses on collaboration between development and operations teams for continuous delivery. | Best for projects requiring continuous integration. | Faster releases, improved system reliability. |
| Spiral | Combines iterative development with systematic risk management at each phase of development. | Best for large, high-risk projects. | Risk management, flexible requirements. |
| V-Model | An extension of the Waterfall model, with corresponding testing phases for each development stage. | Best for projects with strict regulatory compliance. | Rigorous testing, clear steps. |
Tools and Technologies Powering Modern Software
To build efficient and scalable applications, modern software development relies on a wide range of tools and technologies that enable seamless integration, automation, and optimization.
- Languages: Java, Python, C#, Swift
- Frameworks: Angular, React, Django, .NET
- DevOps Tools: Docker, Kubernetes, Jenkins, Git
- AI & Automation: Machine learning and generative AI now assist with testing, code generation, and performance monitoring
With the right stack, businesses can optimize everything from system performance to customer-facing features.
For example, integrating your platform with Email Marketing Services can deliver a seamless omnichannel experience that nurtures leads automatically.
4 Challenges & Success Strategies
Despite the promise of innovation, software development has its challenges:
- Scope creep due to undefined requirements
- Poor communication between technical and non-technical teams
- Security vulnerabilities in rapidly deployed code
- Integration issues with legacy systems
To overcome these, companies must adopt disciplined planning, frequent testing, and security-first principles.
Success also hinges on collaboration between departments, where marketers might check Google keyword ranking to align SEO efforts with product messaging, including marketing, development, and IT, a space where Content Marketing Services can align product value with user education and adoption.
Business Software Development: A Strategic Lever
Unlike generic tools, custom-built software allows organizations to:
- Automate manual tasks
- Centralize data analytics
- Enhance compliance and reporting
- Improve customer and employee experience
Customization is especially valuable in B2B settings, where website development services are crucial to align with complex sales cycles and integration requirements.
6 Major Roles in a Software Development Team
This table helps to clarify the different roles in a development team and their responsibilities.
| Role | Responsibilities | Skills Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Project Manager | Oversees project planning, execution, and delivery, ensuring timelines and budget. | Leadership, communication, project management tools. |
| Business Analyst | Works with stakeholders to gather requirements and define project scope. | Analytical skills, communication, requirement gathering. |
| Software Developer | Writes the code and builds the software according to design specifications. | Programming, problem-solving, development frameworks. |
| QA Engineer | Tests the software for bugs and ensures quality assurance throughout the lifecycle. | Testing methodologies, attention to detail, automation. |
| UI/UX Designer | Designs the user interface and ensures the user experience is intuitive and efficient. | Graphic design, prototyping, user-centered design. |
| System Architect | Defines the system architecture, including hardware, software, and network requirements. | System design, networking, architecture tools. |
Choosing the Right Development Partner
To get the most out of custom development, choosing the right partner is essential. Look for:
- Cross-functional expertise
- Proven design and deployment capabilities
- Business-aligned delivery models
- Post-launch support and optimization
Centric brings this all together with integrated web design and mobile development services, data-driven search engine optimization services, and seamless project execution through our creative services. Whether you're launching a platform, automating a workflow, or expanding into new markets, we help turn your digital vision into reality.
FAQs
What is an example of software development?
An example of software development is creating a mobile app, like a weather forecasting application. The process involves writing code, designing the user interface, testing the app for bugs, and deploying it to app stores. This includes using programming languages, frameworks, and tools to build a fully functional and user-friendly app.
What is the difference between software development and software engineering?
Software development focuses on creating software, while software engineering applies engineering principles to design, develop, and maintain scalable and reliable software.
Why is software development important for businesses?
Software development helps businesses improve efficiency, innovate, and create custom solutions that give them a competitive advantage.
What programming languages are used in software development?
Common programming languages include Python, JavaScript, Java, C++, and Ruby, each suited for specific types of software like web or mobile apps.
Conclusion
What is software development? It’s the fusion of engineering discipline, creative vision, and strategic thinking, purposefully applied to solve business challenges, accelerate growth, and future-proof organizations. It’s no longer limited to coding applications; today, software development is about creating dynamic systems that enable scale, enhance customer experiences, and streamline operations across industries.
In an environment where digital agility defines success, the right software can give businesses a measurable edge. When tailored to your specific goals, it drives productivity, strengthens infrastructure, and unlocks new value at every level. Done well, software becomes more than a product, it becomes a core business asset, supporting innovation and competitive advantage for years to come.
This is where Centric comes in. With a full-service approach that blends deep technical expertise with design and strategy, we help businesses build custom solutions that are not only functional but transformational.From concept to execution, we turn your ideas into high-performing platforms that scale with your vision.