Imagine accessing all your files, software, and business tools from anywhere in the world, without worrying about storage limitations, security, or expensive IT infrastructure. That’s the power of cloud computing.
It has revolutionized how businesses and individuals store data, run applications, and collaborate online. Whether you’re streaming Netflix, using custom web design solutions, or backing up files on Google Drive, cloud technology is at the core of these everyday digital experiences.
In this article, we’ll break down what is cloud computing, how it works, and why businesses are rapidly shifting to cloud-based solutions. We’ll also explore its security, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
You can be a business owner, developer, or just someone curious about the digital world; understanding cloud computing is essential in today’s tech-driven landscape.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics over the internet, commonly referred to as the cloud.
Unlike traditional IT setups that require physical hardware and on-site management, cloud-based computing allows users to access powerful resources on demand, without the need for costly infrastructure.
This transformative cloud technology enables businesses and individuals to store data, run applications, and collaborate seamlessly from any location.
So, what is the cloud? Simply put, it’s a network of remote servers hosted in data centers worldwide, managed by cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
These cloud platforms provide cloud computing solutions that are scalable, secure, and cost-efficient, catering to diverse needs from business cloud services like eCommerce platforms to personal tools like cloud-based software (e.g., Google Docs or Dropbox).
The cloud computing definition hinges on its ability to offer cloud services on a pay-as-you-go basis, ensuring users only pay for the resources they use.
Whether it’s an IT cloud solution for enterprise data management or a cloud-based solution for a startup’s CRM, cloud computing platforms empower users with flexibility and innovation.
As IBM explains, cloud computing allows organizations to focus on their core business by offloading infrastructure management, making it a cornerstone of digital transformation.
How Does Cloud Computing Work?
At its core, cloud computing operates through a network of remote servers hosted in data centers, managed by leading cloud service providers.
These cloud platforms store, process, and manage data, eliminating the need for local servers or personal computers.
Instead of running resource-intensive applications on your device, you access cloud-based software or services via the internet, paying only for what you use.
For example, in business cloud services, an eCommerce platform can store product images, customer data, and transaction records in the cloud, ensuring seamless access from any location.
This IT cloud solution enhances accessibility, supports real-time collaboration, and streamlines operations.
Teams can use cloud-based solutions for tasks like document editing, video conferencing, or managing digital workflows, making cloud computing platforms essential for remote work and global collaboration.
According to IBM, cloud computing allows organizations to focus on innovation by offloading infrastructure management to providers, enabling rapid deployment of applications and services.
This flexibility makes cloud solutions ideal for businesses of all sizes, from startups to enterprises.
Key Queries Addressed
-
What is a cloud? A metaphor for internet-based infrastructure delivering cloud services like storage and processing.
-
Cloud computing meaning: The practice of using remote servers to store, manage, and process data, offering scalability over traditional IT.
- Cloud definition: A network of remote servers providing on-demand computing resources via the internet.
Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing solutions are categorized into three primary types, each offering distinct levels of control, flexibility, and management. Below is a breakdown of these types, followed by a chart for clarity:

1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides businesses with virtualized computing resources over the internet. Companies no longer need to invest in expensive physical servers. Instead, they rent computing power, storage, and networking from cloud providers.
Example: AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud provide IaaS services, allowing companies to run applications without managing the underlying hardware.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers a complete development environment in the cloud. Businesses can build, test, and deploy applications without handling the infrastructure. This model simplifies software development by providing pre-configured tools and frameworks.
Example: Developers use PaaS platforms like Google App Engine and Heroku to build applications quickly without worrying about server management.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is the most common cloud computing model, offering ready-to-use software applications over the internet. Users don’t need to install programs on their computers. Instead, they can access applications directly through web browsers. SaaS applications can also integrate enterprise level SEO strategies to improve online visibility and enhance business growth, particularly for e-commerce platforms and digital marketing efforts.
Example: Digital Marketing Strategy tools like LinkedIn Marketing and B2B Marketing are SaaS applications businesses use for collaboration, file storage, and customer relationship management. SaaS applications help to enhance e-commerce Marketing and Programmatic SEO.
Visualizing Cloud Computing Types
Below is a chart summarizing the differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS:
|
Type |
Description |
Examples |
Use Case |
|
IaaS |
Virtualized computing resources |
AWS EC2, Azure, Google Cloud |
Hosting websites, data storage |
|
PaaS |
Development environment in the cloud |
Google App Engine, Heroku |
App development, testing |
|
SaaS |
Ready-to-use software over the internet |
Salesforce, Dropbox, Google Docs |
Collaboration, CRM, marketing |
This chart highlights how each cloud service caters to different needs, making it easier to choose the right cloud solution for your business.
5 Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses store, manage, and process data. Unlike traditional computing models that require physical infrastructure, cloud computing provides flexible, scalable, and cost-efficient solutions. What makes cloud computing so powerful is its unique set of characteristics that enable seamless digital operations for businesses of all sizes. These features define how cloud services operate and deliver value to users worldwide.
Understanding these key characteristics helps businesses and individuals make informed decisions about adopting cloud-based solutions. Let’s explore the fundamental traits that make cloud computing an essential part of modern digital ecosystems.
1. On-Demand Self-Service
One of the most significant advantages of cloud computing is its ability to provide on-demand self-service. This means that businesses and individuals can access and manage computing resources without direct human intervention from the service provider.
For example, companies can instantly deploy virtual machines, increase storage capacity, or scale computing power without requiring IT teams to manually set up infrastructure.
This self-service model enables businesses to be more agile and responsive to changing needs, eliminating delays caused by manual provisioning.
A great example is the use of cloud-based monitoring solutions that allow businesses to track website performance, troubleshoot issues, and optimize user experiences without needing to install software on local servers.
Additionally, using custom web design services can further enhance these cloud-based solutions by ensuring the website is optimized for cloud functionalities, improving user interaction.
2. Broad Network Access
Another defining feature of cloud computing is broad network access. Cloud services are available over the internet, meaning users can access applications and data from anywhere, anytime, using any device.
This characteristic has enabled the rise of remote work and global collaboration. Employees no longer need to be physically present in an office to access company resources.
Instead, they can log in from their laptops, tablets, even mobile apps & phones to stay connected with teams, access business applications, and manage operations on the go.
Businesses also leverage custom website design to optimize cloud-based applications, ensuring smooth access across different platforms.
Integrating application development services helps enhance this accessibility by providing tailored solutions that meet specific business needs and improve user experience.
3. Resource Pooling
Cloud computing operates on a multi-tenant model, where computing resources are pooled together to serve multiple users dynamically. Instead of allocating dedicated resources for each individual business, cloud providers optimize hardware utilization by distributing workloads across shared infrastructure.
This ensures efficient resource allocation, leading to lower operational costs for businesses. Users don’t have to worry about hardware maintenance, software updates, or server management, the cloud provider handles everything.
For example, cloud-based digital asset management platforms allow businesses to store, organize, and retrieve content efficiently, utilizing shared resources without compromising security.
4. Rapid Elasticity
One of the defining strengths of cloud computing is rapid elasticity, which allows businesses to scale resources up or down instantly based on demand.
In traditional IT environments, companies needed to invest in excess infrastructure to handle potential traffic spikes. However, cloud platforms offer dynamic scalability, meaning resources automatically adjust to fluctuating demands.
For instance, during seasonal shopping events like Black Friday, eCommerce Marketing ensures these businesses can increase server capacity instantly to accommodate the surge in users and then scale down after the event to avoid unnecessary costs.
5. Measured Service
Cloud computing follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model, meaning users only pay for the resources they consume. This measured service approach ensures that businesses can track usage, monitor expenses, and optimize resource allocation for maximum cost efficiency.
Unlike traditional IT setups, where companies had to purchase expensive hardware upfront, cloud computing eliminates unnecessary spending. Cloud providers offer detailed usage reports and analytics, helping businesses fine-tune their resource consumption based on real-time data.
For example, businesses that use SharePoint Custom Portal Services can monitor their cloud expenses and switch between providers to optimize costs.
4 Benefits of Cloud Computing
The rise of cloud computing has changed the way businesses operate, offering multiple advantages that improve efficiency, security, and scalability. Some of the key benefits include:
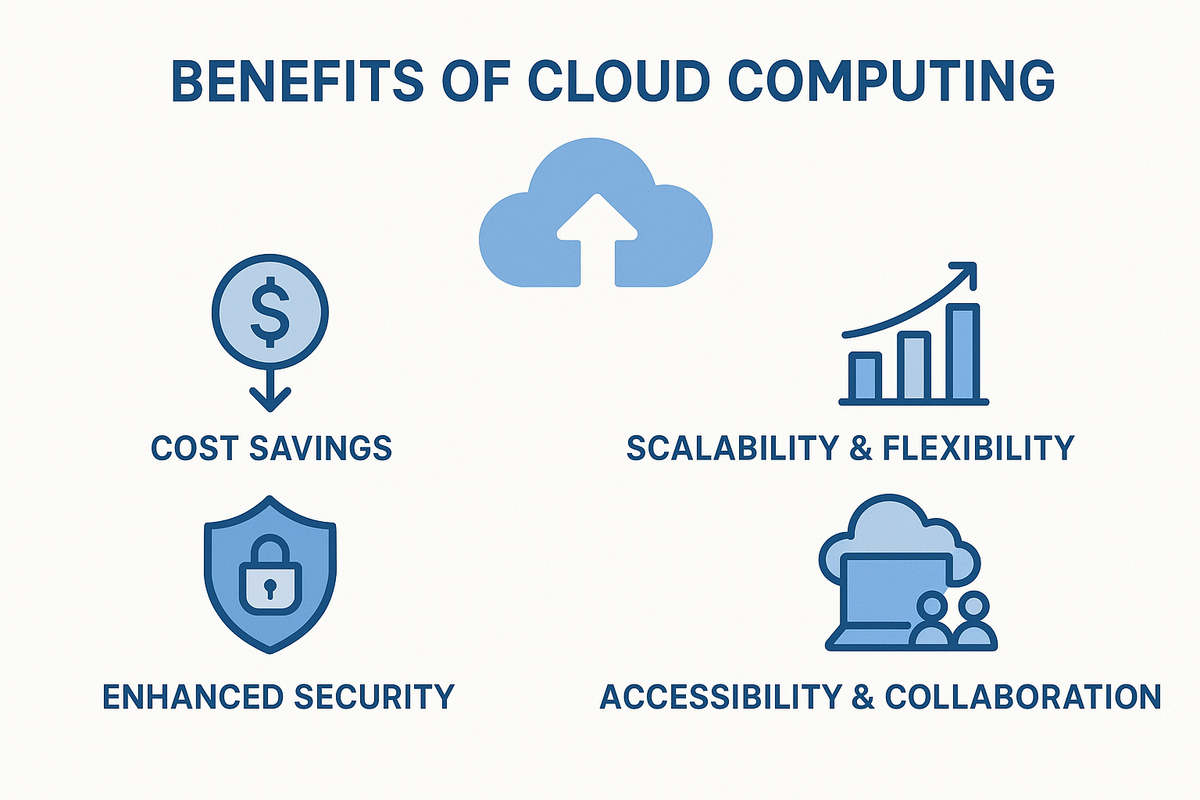
1. Cost Savings
Companies save money by eliminating the need for expensive hardware, maintenance, and IT staff. Cloud providers offer pay-as-you-go pricing, so businesses only pay for the resources they use.
2. Scalability & Flexibility
Cloud computing allows businesses to scale resources up or down based on demand. Whether a company needs extra computing power during peak seasons or wants to reduce costs during slow periods, the cloud provides unmatched flexibility.
3. Enhanced Security
Leading cloud providers implement advanced security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular security updates. This protects sensitive business data from cyber threats.
4. Accessibility & Collaboration
With cloud computing, employees can access data and applications from anywhere, enabling remote work and real-time collaboration. This has become essential for businesses with global teams. Additionally, integrating SEO for enterprise helps businesses optimize their cloud-hosted content for better search engine visibility, making it easier for potential clients to find their services.
3 Challenges of Cloud Computing
Despite its many advantages, cloud computing comes with challenges that businesses must consider.
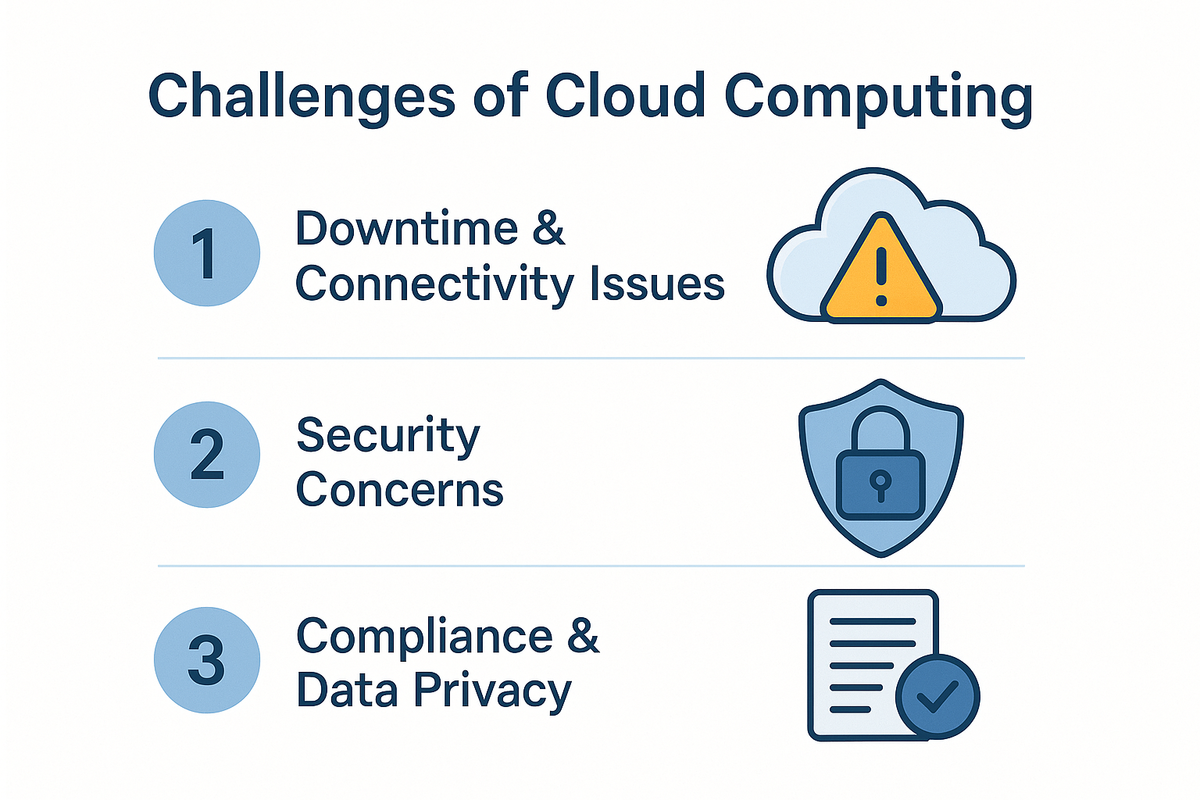
1. Downtime & Connectivity Issues
Since cloud services rely on the internet, businesses may experience downtime during outages or network failures. Companies must have backup plans to ensure uninterrupted operations.
2. Security Concerns
Although cloud security is strong, data stored in the cloud is still vulnerable to cyberattacks. Businesses must implement additional security measures, such as multi-factor authentication and encryption, to protect sensitive information.
3. Compliance & Data Privacy
Different countries have strict data protection laws, requiring businesses to comply with regulations when storing customer data in the cloud. Companies must ensure they follow legal guidelines to avoid penalties.
Future of Cloud Computing
The future of cloud computing is evolving rapidly, with emerging technologies transforming the way businesses manage data, applications, and digital workflows.
As industries continue to embrace cloud-based solutions, advancements such as edge computing, artificial intelligence (AI), hybrid cloud strategies, and boosted security measures are shaping the next generation of cloud computing. A critical aspect of this evolution is understanding the differences between Machine Learning vs Deep Learning, as these technologies are being increasingly integrated into cloud platforms to drive automation, optimize business processes, and enhance decision-making capabilities.
1. Edge Computing: Bringing Data Closer to Users
One of the most significant shifts in cloud computing is edge computing. Traditionally, cloud data is stored and processed in centralized data centers, which can sometimes cause latency issues, especially for real-time applications. Edge computing solves this by moving data processing closer to the user, reducing delays and enhancing performance.
Industries such as healthcare, autonomous vehicles, and the Internet of Things (IoT) rely on instant data processing, making edge computing a game-changer.
For example, self-driving cars need real-time data processing to make split-second decisions, and cloud computing ensures that this data is analyzed instantly at the edge rather than being sent to a distant server.
2. AI & Machine Learning: Enhancing Cloud Automation
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are now deeply integrated into cloud computing platforms, allowing businesses to automate processes, analyze large data sets, and enhance security. AI-driven cloud solutions provide predictive analytics, real-time fraud detection, and automated decision-making that improve efficiency.
For instance, AI in eCommerce Marketing can optimize customer experience by personalizing website content, ensuring that users receive relevant information based on their behavior. Businesses also utilize machine learning in cloud-based Digital Marketing Strategy, improving how they organize and retrieve content.
3. Hybrid & Multi-Cloud Strategies: The New Standard for Businesses
As businesses grow, their need for scalable, flexible cloud solutions increases. Many organizations are moving toward hybrid and multi-cloud strategies to balance security, cost-efficiency, and performance.
A hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud environments, allowing companies to store sensitive data on private servers while using public clouds for scalability.
On the other hand, multi-cloud strategies involve using multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and increase system reliability.
For example, e-commerce businesses use hybrid clouds to manage sensitive customer data while leveraging public cloud resources to handle high website traffic. This ensures data security while maintaining smooth user experiences. Investing in ui design services also plays a crucial role in ensuring that the interfaces between these cloud systems remain user-friendly, enhancing the overall digital experience for end-users.
4. Stronger Cloud Security & Compliance
With increasing cybersecurity threats, cloud providers are investing heavily in advanced security solutions such as zero-trust architectures, end-to-end encryption, and AI-driven threat detection.
Companies are also focusing on regulatory compliance, ensuring that cloud storage, data transfers, and processing meet legal requirements. Cloud security advancements will make data protection and risk mitigation a priority in the coming years.
Why Businesses Are Shifting to Cloud Solutions?
The cloud meaning goes beyond technology it’s a strategic shift toward efficiency and growth. Cloud computing solutions empower businesses to:
-
Streamline operations with cloud-based software for workflows and automation.
-
Enhance eCommerce SEO by hosting digital assets in the cloud for faster access.
-
Support global teams with cloud platforms for seamless collaboration.
-
Drive digital transformation with scalable IT cloud solutions.
For example, Centric leverages cloud technology to deliver tailored digital experiences, from SharePoint consulting to eCommerce portal development, helping businesses stay competitive.
How to Choose the Right Cloud Solution?
Selecting the right cloud service depends on your business needs:
-
Startups: Opt for SaaS for cost-effective, ready-to-use tools like CRM or marketing platforms.
-
Developers: Choose PaaS for streamlined app development without infrastructure hassles.
-
Enterprises: Use IaaS for customizable, scalable infrastructure to support complex operations.
Evaluate providers based on security, scalability, and pricing. Leading cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer robust cloud computing platforms tailored to various industries.
FAQs
What is Cloud Computing in Simple Terms?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services like storage, software, and processing power over the internet, allowing users to access these resources without owning physical hardware. It’s like renting computer resources from a remote data center, managed by providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud, on a pay-as-you-go basis. This makes it easy to store data, run applications, and collaborate from anywhere.
What is the best Example of Cloud Computing?
An example of cloud computing is Google Drive, where you can store files, access them from any device with an internet connection, and share them with others. Instead of saving files on your computer’s hard drive, they’re stored on Google’s remote servers, making it convenient and accessible.
Is Cloud Computing Easy?
Cloud computing can be easy to use, especially for end-users leveraging SaaS applications like Google Docs or Dropbox, which require minimal technical knowledge. The blog highlights the on-demand self-service and broad network access characteristics, meaning users can quickly access resources from any device without complex setup. However, for businesses implementing IaaS or PaaS, it may require technical expertise to configure and manage, though cloud providers simplify this with user-friendly interfaces and support.
Final Thoughts
What is cloud computing? It is more than just storing data on remote servers; it is a fundamental shift in how businesses and individuals operate in the digital world.
Cloud computing has transformed industries by offering scalability, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced security, allowing businesses to innovate and grow without the limitations of traditional IT infrastructure.
As technology advances, the future of cloud computing will be shaped by edge computing, AI-driven automation, and hybrid cloud strategies. Businesses that adopt these advancements will gain a competitive edge by optimizing workflows, improving collaboration, and ensuring easy access to data and applications.
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, cloud computing is not just an option; it is a necessity. Companies that integrate cloud-based solutions into their operations will remain agile, efficient, and prepared for the future.
It can be for custom web design, digital asset management, or advanced security solutions, cloud technology continues to redefine how we work, connect, and innovate.